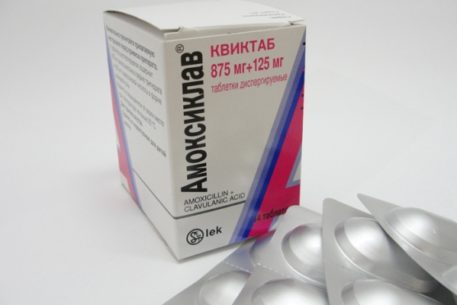
As statistics show, most common diseases are the result of a bacterial invasion of the body. The list of the most important drugs recommended by WHO for the treatment of bacterial infections includes Amoxiclav.
This medicine was created specifically to combat strains that most often affect humans, and can not only inhibit the activity of pathogenic microorganisms, but also enhance the body's overall opposition to bacterial aggression.
Material Content:
- 1 Composition and forms of antibiotic release
- 2 Pharmacological properties and indications for use
- 3 Instructions for use Amoxiclav for children and adults
- 4 Contraindications, side effects and overdose
- 5 Amoxiclav during pregnancy and lactation
- 6 Can I drink alcohol while taking the drug
- 7 Drug Interactions with Other Drugs
- 8 Analogues of the antibiotic Amoxiclav
- 9 Comparison with other drugs
Composition and forms of antibiotic release
Amoxiclav is a medicine combined from two pharmaceuticals of the antibacterial group - Amoxicillin and Clavulanic acid. The composition of the drug contains two active compounds - amoxicillin trihydrate and potassium salt of clavulanic acid.
The ratio between amoxicillin trihydrate and the potassium salt of clavulanic acid in the drug is determined by its pharmaceutical form and may be:
- in film-coated tablets, from 250 mg / 125 mg to 875 mg / 125 mg;
- in powder for suspension preparation (per 5 ml) - from 156.25 mg / 31-5 mg to 250 mg / 62.5 mg;
- in dispersible tablets (Amoxiclav Quicktab) - from 574 mg / 148.87 mg to 1004.50 mg / 148.87 mg;
- in powder for infusion (one bottle) - from 500 mg / 100 mg to 1000 mg / 200 mg.
The medicine also contains various additional substances and inactive flavoring additives.
On the surface of the tablets in the film shell there is an imprint indicating the number of active compounds and the abbreviation of the name AMS.
Pharmacological properties and indications for use
Amoxiclav is a broad-spectrum bactericidal antibacterial agent.
Due to the combination of two compounds, Amoxiclav is characterized by the characteristics of each of them, which provides a double effect of the therapeutic effect of the drug.
Pharmacology Amoxicillin
Amoxicillin in the composition of the drug is an antibiotic obtained synthetically. It belongs to the group of penicillins - organic compounds isolated from mold cultures.
A characteristic feature of Amoxicillin is the presence in its formula of a hydroxyl group that provides rapid absorption of the drug.
Pharmacological characteristics of Amoxicillin:
- penetrates the membrane of bacterial cells and binds enzymes necessary to maintain the strength of cell walls;
- disrupts the processes associated with the reproduction and growth of bacteria;
- promotes the dissolution of bacterial cells and their systems.
Amoxicillin affects staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci, Escherichia coli, Shigella, Salmonella and Klebsiella enterobacteria.
Some bacteria produce beta-lactamases, which provide resistance to Amoxicillin, which can be neutralized by a combination of the drug with clavulanic acid.
Pharmacological features of clavulanic acid
The clavulanic acid compound is able to suppress beta-lactamases - bacterial enzymes responsible for the resistance of microorganisms when exposed to penicillin antibiotics.
The pronounced antimicrobial effect of clavulanic acid is due to the beta-lactam structure. In addition, the compound has specific properties:
- provides antibacterial activity;
- strengthens antimicrobial immunity;
- interacts with penicillin-binding proteins of microorganisms;
- causes lysis processes in the cell membrane of bacteria.
The most pronounced effect of clavulanic acid is manifested in relation to staphylococci, streptococci, gonococci, chlamydia and legionella. To a lesser extent, clavulanate is able to affect the vital activity of Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae and Enterococci.
Clavulanic acid expands the spectrum of action of amoxicillin, providing a high level of clinical efficacy of Amoxiclav.
Nosological classification (ICD-10)
According to the nosological classification of diseases adopted by the world medical community, the antibiotic Amoxiclav is prescribed for such pathological processes as:
- various types of otitis media - moderate, acute, unspecified, purulent;
- sinusitis, tonsillitis, pharyngitis - of all types and forms;
- abscesses - retropharyngeal, parapharyngeal;
- unspecified lesions of the upper respiratory tract;
- unspecified bronchitis and pneumonia;
- skin infections;
- infectious arthritis;
- cholecystitis;
- obstructive pulmonary disease - of all kinds;
- cholangitis;
- peptic ulcer caused by defeat Helicobacter pylori;
- osteomyelitis;
- urinary and genital infections, including sexually transmitted infections;
- bites of poisonous insects and snakes.
Along with the, Amoxiclav is used for soft tissue lesions arising from the above pathologies and for the prevention of postoperative infections.
Pharmacokinetics of the drug
The pharmacokinetics of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid are very similar. Both compounds dissolve in the aquatic environment and are rapidly absorbed into the blood, provided that they are taken before eating.
The highest level of active compounds is observed in the blood an hour after application. Substances are evenly distributed not only in all organs, but also in the fluids present in the body.
Amoxiclav is able to overcome the blood-brain barrier only in the presence of inflammation of the meninges.
The excretion of metabolites occurs naturally in the period t two to six hours after absorption.
Instructions for use Amoxiclav for children and adults
The questions of the exact dosage of Amoxiclav are decided by the attending physician, however, the volume of the drug prescribed for a single dose should not be lower than the values indicated by the instructions for use. Otherwise, the level of therapeutic effect achieved will be insufficient.
Amoxiclav tablets
Doctors recommend taking Amoxiclav tablets for adults and children from the age of six.
The following daily dosage is considered optimal:
- children from six to twelve years old - 40 mg per kg of weight;
- for children over 40 kg and for adults, one 250 mg / 125 mg tablet every eight hours for simple infections. With complex lesions, the dose is increased by the attending physician.
The tablet form of the drug must be taken in its entirety, without grinding and drinking with water immediately before meals. The optimal course is two weeks.
Amoxiclav Quiktab Dispersible Tablets are only allowed for patients under 12 years of age - a 500 mg / 125 mg tablet every 12 hours.
The tool is taken, after dissolving the tablet in 30 ml of water.
Amoxiclav suspension for children
To facilitate the administration of the drug by children under six years of age, Amoxiclav suspension for children is provided.
The daily dose for babies up to three months is divided into two doses - at the rate of 30 mg per kg of weight.
A single dosage for children whose weight has reached five kilograms is determined on the basis of indicators of weight, and not the age of the child. The severity of the disease is also taken into account:
- 5-10 kg - 1.25 ml-2.5 ml;
- 10-15 kg - 2.5 ml-3.75 ml;
- 15-20 kg - 3.75 ml-5.0 ml;
- 20-30 kg - 5.0 ml-7.5 ml;
- 30-40 kg - 6.5 ml-10.0 ml.
The suspension is taken twice a day. Dosing of the suspension is carried out using a pipette, which is included in each package of the product.
To obtain a suspension, shake the vial with the powder and add the required amount of water, indicated in the instructions for the drug. Shake again. For ease of volume measurement, a graduation scale is placed on the bottle.
The total daily dose for children under six years old cannot exceed 45 mg per kilogram of the baby’s weight.
Lyophilized powder for injection
The dosage of the intravenous solution depends on the weight of the child and the characteristics of the course of the disease.
Standard doses are:
- up to 40 kg - 30 mg per kg twice a day if the child weighs less than 4 kg and three times a day if the child weighs more than 4 kg;
- adults and children weighing more than 40 kg are given 1.2 g of the drug every eight hours.
To prepare an injection, the contents of a 600 mg vial are mixed with 10 ml of water for injection. For drip administration, a solution prepared for intravenous use is mixed with 50 ml of an infusion solution.
Amoxiclav intravenous solutions are strictly forbidden to be administered intramuscularly.
Contraindications, side effects and overdose
Amoxiclav treatment is undesirable if the patient has such pathologies as:
- liver dysfunction;
- kidney failure;
- lymphocytic leukemia;
- an allergic reaction to antibiotics containing cephalosporin;
- mononucleosis.
A sharp deterioration in the patient’s well-being after taking the drug is a sign of the development of adverse reactions. Typically, such complications manifest as nausea, itchy skin rashes, diarrhea, abdominal pain, swelling, dizziness, and seizures.
Less commonly observed changes in the composition of the blood and dysfunction of the nervous system in the form of increased activity, excitability, anxiety conditions.
Amoxiclav during pregnancy and lactation
Treatment with Amoxiclav during pregnancy is possible, but undesirable, since the active compounds of the drug have the ability to penetrate into breast milk. The use of the drug is allowed in cases of a high degree of threat to the health of the mother.

Can I drink alcohol while taking the drug
The use of alcoholic beverages is unacceptable not only during the use of Amoxiclav, but also within a week after the completion of the therapeutic course.

Taking Amoxiclav and alcoholic beverages causes the development of acute intoxication syndrome. The accumulation of acetaldehyde in the tissues of the body and the increase in the toxic effect that is observed in such cases can cause death.
Drug Interactions with Other Drugs
The use of Amoxiclav simultaneously with other types of drugs is not always justified, since the active compounds react, and their pharmacological properties change.
Interaction with various medicines can be expressed in:
- reduced absorption - aminoglycosides, glucosamines, antacids;
- increased absorption - ascorbic acid;
- an increase in the concentration of amoxicillin - Allopurinol, Phenylbutazone or diuretics;
- bleeding - ethinyl estradiol;
- lowering the antibacterial effectiveness of Amoxiclav - Rifampicin, macrolides, tetracyclines, sulfonamides.
Amoxiclav, in turn, slows down the effects of oral contraceptives.
Analogues of the antibiotic Amoxiclav
Absolute analogues of Amoxiclav are drugs whose action is based on a combination of amoxicillin and clavulanic acid compounds.
Augmentin is considered the official predecessor of Amoxiclav - under this name in 1984 the original drug invented by British pharmacists was registered.
Also, the drug is known under such trade names as Amoxil-K, Clavomed, Flemoklav Solutab, KLAMP, Klavamoks.
Comparison with other drugs
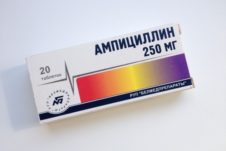
By pharmacological properties, Amoxiclav is closest to Amoxicillin and Ampicillin. However, a comparison of the therapeutic possibilities of these drugs shows significant differences, mainly in favor of Amoxiclav.
Amoxicillin and Ampicillin are not able to affect microorganisms that produce beta-lactamases. While the resistance of Amoxiclav to beta-lactamases is due to the properties of clavulanic acid.
Thus, due to the presence of clavulanate in the composition of the drug, the possibilities for its effect have become more significant.
In addition, due to the presence of a hydroxyl group in the amoxicillin compound, the absorption rate and oral bioavailability of Amoxiclav are an order of magnitude higher than that of Ampicillin.
The only "drawback" of Amoxiclav is the higher cost compared to Amoxicillin and Ampicillin. However, the significance of this minus is lost amid the health benefits that Amoxiclav treatment provides.